 |
| Technical Analysis |
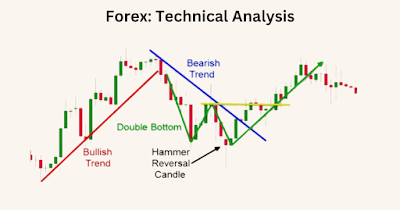
Forex: Technical Analysis
- Definition of Technical Analysis
- Basic Assumptions of Technical Analysis
- Technical Analysis Tools
- Types of Technical Analysis
- Common Technical Analysis Strategies
- Criticisms of Technical Analysis
- Conclusion
Definition of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating and forecasting
the price movements of financial assets, such as stocks, currencies, and
commodities, by analyzing past market data, primarily price and volume, to
identify patterns, trends, and indicators that can help predict future price
movements. Technical analysts believe that historical price and volume data can
provide insights into the underlying supply and demand dynamics of an asset and
that patterns and trends can help identify potential opportunities for buying
or selling. Technical analysis is widely used in financial markets and is often
used in conjunction with fundamental analysis, which focuses on analyzing the
underlying economic and financial factors that can impact an asset's price.
Basic Assumptions of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is based on several key assumptions:
1. Market action discounts everything: The price of an
asset reflects all available information, including economic data, news events,
and market sentiment. Technical analysts believe that price movements are not
random, but instead reflect the supply and demand forces that drive the market.
2. Prices move in trends: Technical analysts believe
that markets tend to move in trends, and that these trends can be identified
and traded. They use various tools and techniques to identify the direction and
strength of a trend, and to determine when it may be ending or reversing.
3. History tends to repeat itself: Technical analysts
believe that market patterns and trends tend to repeat themselves over time,
due to the underlying human psychology and behavior that drives market
movements. They use historical data to identify patterns and trends, and to
make predictions about future price movements.
4. Technical analysis can be applied to any market:
Technical analysis is not limited to any particular market or asset class, but
can be applied to stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies, among others.
Technical analysts use similar tools and techniques across different markets,
with the goal of identifying profitable trading opportunities.
Overall, the basic assumptions of technical analysis are that
the market reflects all available information, that prices move in trends, that
history tends to repeat itself, and that technical analysis can be applied to
any market. By understanding these assumptions, traders can use technical
analysis to identify profitable trading opportunities and make informed trading
decisions.
Technical Analysis Tools
a. Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs are a fundamental tool in technical
analysis, as they allow traders to visualize market data over time and identify
patterns, trends, and potential trading opportunities. Some of the most common
types of charts and graphs used in technical analysis include:
1. Line charts: This type of chart is created by
connecting a series of data points with a line. It is often used to show
long-term trends in price movements.
2. Bar charts: This type of chart displays price
information for a specified time period in the form of vertical bars. The top
of each bar represents the highest price of the asset during that period, while
the bottom represents the lowest price.
3. Candlestick charts: This type of chart is similar
to bar charts, but is more visually appealing and easier to interpret. Each
candlestick represents a time period (e.g., one day) and shows the
opening and closing price, as well as the high and low price for that period.
4. Point and figure charts: This type of chart is used
to identify long-term trends and reversals. It consists of columns of X's and
O's, with X's representing an upward movement in price and O's representing a
downward movement.
Traders use these charts and graphs to identify various
patterns and trends, such as support and resistance levels, chart formations
like head and shoulders, and trend lines. By analyzing these patterns, traders
can identify potential entry and exit points for trades.
b. Trend Lines
Trend lines are an important tool used in technical analysis
to identify and confirm the direction of a trend in a financial market. A trend
line is simply a straight line that connects two or more price points on a
chart. The primary purpose of a trend line is to identify the direction of a
trend and to help traders identify potential areas of support and resistance.
In an uptrend, a trend line is drawn below the price action
by connecting two or more low points. In a downtrend, a trend line is drawn
above the price action by connecting two or more high points. When prices
approach a trend line, traders look for potential areas of support or
resistance. If prices break through a trend line, it may signal a change in the
direction of the trend.
It is important to note that trend lines are subjective and
can vary from trader to trader. Traders may draw different trend lines based on
their interpretation of the price action, which can result in different trading
signals. Therefore, it is important to use trend lines in conjunction with
other technical indicators and analysis tools to make informed trading
decisions.
c. Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are key concepts in technical
analysis that help traders identify potential levels of buying and selling in a
market.
Support levels are price levels at which a currency pair has
historically found buyers and is expected to stop falling in price, as demand
for the currency increases. Resistance levels, on the other hand, are price
levels at which a currency pair has historically found sellers and is expected
to stop rising in price, as supply of the currency increases.
When a support or resistance level is breached, it can
indicate a change in market sentiment and potentially signal a new trend
direction. Support and resistance levels can be identified through chart
analysis and can be used to determine entry and exit points for trades.
d. Moving Averages
Moving averages are commonly used technical analysis tools
that are used to smooth out price trends by filtering out noise from short-term
price fluctuations. A moving average is the average price of an asset over a
certain period of time, with the most recent prices given more weight. Moving
averages are used to identify the direction of the trend and potential areas of
support or resistance.
There are several types of moving averages, including simple
moving averages (SMA), exponential moving averages (EMA), and
weighted moving averages (WMA). The SMA is calculated by adding up the
closing prices for a certain number of periods and then dividing by the number
of periods. The EMA is calculated by giving more weight to the most recent
prices, while the WMA gives more weight to the most recent and relevant prices.
Moving averages can be used as a standalone indicator, or
they can be used in combination with other technical indicators to generate
trading signals. For example, a trader may look for a crossover of the price
and a moving average as a signal to enter or exit a trade. Moving averages can
also be used to determine potential areas of support or resistance, with the
50-day and 200-day moving averages being particularly popular for this purpose.
e. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a technical momentum
indicator that compares the magnitude of a currency pair's recent gains to the
magnitude of its recent losses and returns a value between 0 and 100. The RSI
is calculated using the average gains and losses over a specified period of
time, typically 14 days.
Traders use the RSI to identify overbought and oversold
conditions in the market. When the RSI is above 70, it is considered
overbought, indicating that the currency pair may be due for a downward
correction. Conversely, when the RSI is below 30, it is considered oversold,
indicating that the currency pair may be due for an upward correction.
In addition to overbought and oversold conditions, traders
may also use the RSI to identify bullish and bearish divergences. A bullish
divergence occurs when the RSI is making higher lows while the price is making
lower lows, indicating that the currency pair may be due for an upward
reversal. A bearish divergence occurs when the RSI is making lower highs while
the price is making higher highs, indicating that the currency pair may be due
for a downward reversal.
f. Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator is a popular momentum indicator
used in technical analysis to identify overbought and oversold conditions in
the market. It measures the relationship between the closing price of an asset
and its price range over a specified period of time. The indicator oscillates
between 0 and 100, with readings above 80 considered overbought and readings
below 20 considered oversold.
The Stochastic Oscillator is calculated using the following
formula:
%K = 100 * [(C – L5close) / (H5 – L5)]
where:
C = the most recent closing price
L5 = the low of the 5 previous
trading sessions
H5 = the high of the 5 previous
trading sessions
%K is the raw value of the
indicator, while %D is a moving average of %K. The most commonly
used %D value is 3.
Traders often use the Stochastic Oscillator in conjunction
with other technical indicators and chart patterns to confirm trading signals
or identify potential reversals in the market.
g. Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci retracement is a technical analysis tool used to
identify potential levels of support and resistance in a market. It is based on
the idea that markets often retrace a predictable portion of a move, after
which they will continue to move in the original direction. The tool is named
after the famous Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci, who discovered a
series of numbers that have since been applied to various aspects of the
financial markets.
In Fibonacci retracement, a trader first identifies a
significant price move and then divides that move into specific percentage
retracements, based on the Fibonacci sequence. The most commonly used
retracement levels are 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%. These levels
are drawn on the chart using horizontal lines to indicate where the price might
find support or resistance as it retraces the move.
Traders use Fibonacci retracement in combination with other
technical analysis tools to identify potential entry and exit points in the
market. The tool can be applied to any market, including stocks, commodities,
and currencies. However, it should be noted that while Fibonacci retracement
can be a useful tool, it is not always accurate and should be used in
combination with other technical analysis tools and market knowledge.
h. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands is a technical analysis tool created by John
Bollinger in the early 1980s. It consists of a set of three lines plotted on a
price chart. The middle line is a moving average, typically set to 20 periods,
while the upper and lower lines are plotted at two standard deviations away
from the moving average.
The Bollinger Bands help traders to identify potential
overbought and oversold conditions in the market. When the price is near the
upper band, it suggests that the asset is overbought and may be due for a price
correction. Conversely, when the price is near the lower band, it suggests that
the asset is oversold and may be due for a price increase.
Traders also use Bollinger Bands to identify trends in the
market. If the bands are widening, it indicates that the market is volatile and
a trend may be forming. If the bands are narrowing, it suggests that the market
is consolidating and a trend may be ending.
Bollinger Bands are a popular tool among traders due to their
simplicity and versatility. They can be used in combination with other
technical indicators to develop trading strategies. However, it's important to
remember that no single indicator can predict market movements with complete
accuracy, and traders should always use caution and risk management strategies
when trading.
i. Japanese Candlesticks
Japanese candlesticks are a popular charting technique used
in technical analysis to visualize the price movement of a financial instrument
over a certain time period. Each candlestick represents a specific time period,
such as one day or one hour, and includes four main points: the opening price,
the closing price, the high price, and the low price.
The body of the candlestick is represented by the opening and
closing prices and is colored differently depending on whether the closing
price is higher or lower than the opening price. If the closing price is higher
than the opening price, the body of the candlestick is typically colored green
or white, while if the closing price is lower than the opening price, the body
of the candlestick is typically colored red or black.
The wicks or shadows of the candlestick represent the high
and low prices for the given time period. The upper wick represents the high
price, while the lower wick represents the low price.
By analyzing patterns and combinations of candlesticks,
traders can identify potential trend reversals or continuation, as well as
support and resistance levels, and make trading decisions accordingly.
Types of Technical Analysis
a. Price Action Analysis
Price action analysis is a trading strategy used by technical
analysts to make trading decisions. It involves analyzing the price movement of
an asset and using that information to predict future price movements.
Price action analysis is based on the idea that the market
price reflects all available information about an asset, including economic,
financial, and political factors. Therefore, the analysis focuses solely on the
price movement of the asset and its historical patterns. This analysis can be
applied to any financial asset, including currency pairs, stocks, and
commodities.
Price action analysis uses a variety of tools, including
support and resistance levels, trend lines, and chart patterns, to identify
price movements and trends. Technical analysts also use indicators such as
moving averages and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm their
analysis.
Price action analysis is a popular trading strategy because
it is simple and effective. It does not require complex mathematical models or
sophisticated algorithms. Instead, it relies on a trader's ability to interpret
market data and make informed decisions. However, it does require a deep
understanding of the markets and a keen eye for detail.
b. Chart Pattern Analysis
Chart pattern analysis is a form of technical analysis used
to identify potential trading opportunities based on patterns formed by the
price movements of a financial instrument, such as a currency pair. Chart
patterns are formed by the recurring shapes and structures that appear on price
charts, and they can signal a reversal or continuation of a trend. There are
several types of chart patterns that traders can use to identify potential
trading opportunities, including:
1. Head and shoulders pattern: A head and shoulders
pattern is a reversal pattern that signals a potential trend change. It
consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being higher than the
other two (the shoulders). Traders may look to enter a short position when the
price breaks below the neckline of the pattern.
2. Double top and double bottom patterns: These are
reversal patterns that form when the price reaches two peaks or two troughs,
respectively, at approximately the same level. Traders may look to enter a
short position when the price breaks below the support level of a double top
pattern, or enter a long position when the price breaks above the resistance
level of a double bottom pattern.
3. Triangle patterns: A triangle pattern is formed by
drawing trend lines that connect a series of highs and lows. There are three
types of triangle patterns: symmetrical, ascending, and descending. Traders may
look to enter a long position when the price breaks above the upper trend line
of a triangle pattern, or enter a short position when the price breaks below
the lower trend line.
4. Flags and pennants: These are continuation patterns
that occur when the price experiences a brief period of consolidation before
resuming its previous trend. Flags and pennants are characterized by a
short-term trend line that runs parallel to the longer-term trend line. Traders
may look to enter a long position when the price breaks above the upper trend
line of a flag or pennant pattern, or enter a short position when the price
breaks below the lower trend line.
5. Wedge patterns: A wedge pattern is a continuation
pattern that occurs when the price consolidates between two trend lines that
converge in either an upward or downward direction. Traders may look to enter a
long position when the price breaks above the upper trend line of a wedge
pattern, or enter a short position when the price breaks below the lower trend
line.
Chart pattern analysis is a popular tool used by technical
traders to identify potential trading opportunities. However, it is important
to note that chart patterns are not always reliable, and traders should always
use additional technical and fundamental analysis to confirm their trading
decisions.
c. Indicator Analysis
Indicator analysis is a technical analysis technique used to
forecast the future price movements of financial assets such as currencies,
stocks, and commodities. Indicators are mathematical calculations based on
price and/or volume data of the underlying asset. Traders use indicators to
analyze the historical price data of an asset and identify potential price
trends or reversals.
There are two types of indicators: leading indicators and
lagging indicators. Leading indicators are designed to identify potential trend
changes before they occur, while lagging indicators are used to confirm trend
changes that have already occurred.
Some of the commonly used technical indicators in forex
trading include Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI),
Stochastic Oscillator, Fibonacci Retracement, Bollinger Bands, and MACD (Moving
Average Convergence Divergence). These indicators can be used in
combination with other technical analysis tools to generate trading signals and
make trading decisions.
Common Technical Analysis Strategies
a. Trend Trading
Trend trading is a strategy in which a trader attempts to
profit from the directional movement of an asset's price. The idea behind trend
trading is to identify a trend in the price movement of an asset, and then to
buy or sell in the direction of that trend in order to capture profits.
Traders who employ this strategy typically use technical
analysis tools and techniques to identify trends, such as moving averages,
trend lines, and other chart patterns. They may also use indicators such as the
Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence
Divergence (MACD) to confirm the strength of a trend.
The basic approach to trend trading is to identify an uptrend
or a downtrend, and then to enter a long or short position accordingly. The
trader will then typically set a stop loss order to limit their potential
losses if the trend reverses, and a profit target to take profits if the trend
continues.
Trend trading can be used in a variety of markets, including
forex, stocks, and commodities. It is important for traders to be patient and
disciplined when employing this strategy, as trends can take time to develop
and may not always be immediately apparent.
b. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading is a trading strategy used by investors to
capitalize on a sudden surge in price after a period of consolidation or
trading within a range. The strategy is based on the assumption that when the
price of an asset breaks out of its trading range, it will continue to move
strongly in the direction of the breakout. Breakout traders typically look for
key levels of support and resistance and buy or sell the asset once it moves
beyond these levels.
For example, if the price of a currency pair has been trading
in a range between 1.2000 and 1.2200 for a period of time, a breakout trader
may wait for the price to move beyond one of these levels before entering a
trade. If the price breaks above 1.2200, the trader may enter a long position
in anticipation of further upward movement. Conversely, if the price breaks
below 1.2000, the trader may enter a short position in anticipation of further
downward movement.
Breakout trading can be applied to various time frames, from
short-term intraday trading to long-term position trading, and can be used in
combination with other technical analysis tools and strategies. However, it is
important to note that breakouts can sometimes be false, and the price may
quickly retreat back into the trading range. Therefore, risk management and
stop loss orders are crucial when using this strategy.
c. Range Trading
Range trading is a type of trading strategy that involves
identifying and trading within a range that a particular asset's price has been
moving in. It is based on the assumption that the price of an asset will remain
within a certain range for a period of time before breaking out in one direction
or the other. In range trading, traders look for support and resistance levels
that define the range of price movement. Once these levels have been
identified, traders will buy at the bottom of the range and sell at the top,
and vice versa, until the price breaks out of the range. This strategy is best
suited for assets that are not experiencing significant price movements in
either direction, and is often used in markets with low volatility. Range
trading is a popular strategy for forex traders, as it allows them to profit
from short-term price movements without exposing themselves to significant
risk.
d. Swing Trading
Swing trading is a trading strategy that involves holding
positions for a few days up to several weeks, in order to capture short-term
price movements in the market. The idea behind swing trading is to identify
trends or price patterns in the market and then take advantage of them by
buying low and selling high (or selling high and buying low for short
positions). Swing traders use technical analysis and chart patterns to
identify potential entry and exit points for their trades, and they often use
stop-loss orders to manage risk. The goal of swing trading is to capture a
portion of a trend or price movement, while avoiding the risks of long-term
holding.
e. Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term trading strategy where
traders aim to hold their positions for weeks, months, or even years. Position
traders typically use fundamental analysis and a macroeconomic approach to
identify potential trades. They look for assets that are undervalued or
overvalued based on their underlying economic fundamentals and hold onto them
for an extended period, waiting for the market to reflect the asset's true
value.
Position traders are less concerned with short-term market
fluctuations and focus on the long-term trend of the asset. They may use
technical analysis to determine the best entry and exit points for their
positions, but the overall strategy is based on long-term market trends rather
than short-term price movements.
Position trading is a popular strategy for investors who have
a long-term investment horizon and are willing to tolerate short-term
volatility in the pursuit of long-term gains. It requires a high level of
patience and discipline, as positions are held for extended periods, and market
fluctuations can be unpredictable.
Criticisms of Technical Analysis
There are some criticisms of technical analysis, which
include:
1. Historical data may not always predict future
performance: Technical analysis is based on the premise that historical
data can be used to predict future market trends. However, this assumption is
not always true, as market conditions can change quickly and unexpectedly.
2. Lack of fundamental analysis: Technical analysis
only considers price and volume data, and does not take into account other
factors that can influence market trends, such as economic indicators or
company performance.
3. Subjectivity: Technical analysis is often
subjective, as different analysts may interpret the same data differently,
leading to differing conclusions about market trends.
4. Over-reliance on indicators: Technical analysts may
rely too heavily on indicators, which can sometimes provide conflicting
signals, leading to confusion and incorrect predictions.
5. False signals: Technical analysis can sometimes
generate false signals, leading traders to make incorrect trading decisions.
For example, a trend may appear to be reversing, when in fact it is just a
temporary pullback.
Despite these criticisms, technical analysis remains a
popular tool among traders, especially in the short-term trading of currencies,
stocks, and other financial instruments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technical analysis is a popular approach used by traders to analyze and predict future price movements of currency pairs in the Forex market. It is based on the assumption that past market trends, along with other technical indicators, can be used to identify future market trends. Various tools, such as charts, trend lines, moving averages, and oscillators, are used to perform technical analysis. Despite its popularity, technical analysis also has its limitations and criticisms, including its subjectivity and the risk of relying too heavily on past price movements. Nonetheless, understanding technical analysis is an important aspect of Forex trading and can be a valuable tool in developing trading strategies and making informed trading decisions.





